DBT Therapy
Understanding DBT Therapy in the Context of Trauma and Mental Health
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a form of psychotherapy that has gained prominence for its effectiveness in treating a range of mental health issues, particularly those rooted in trauma. Developed by Marsha M. Linehan in the late 1980s, DBT combines principles of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with concepts from Eastern mindfulness practices. We will dive into the intricacies of DBT, examining its role and interplay with various aspects of trauma therapy, including PTSD, EMDR, and other therapeutic techniques.
The Core of DBT Therapy
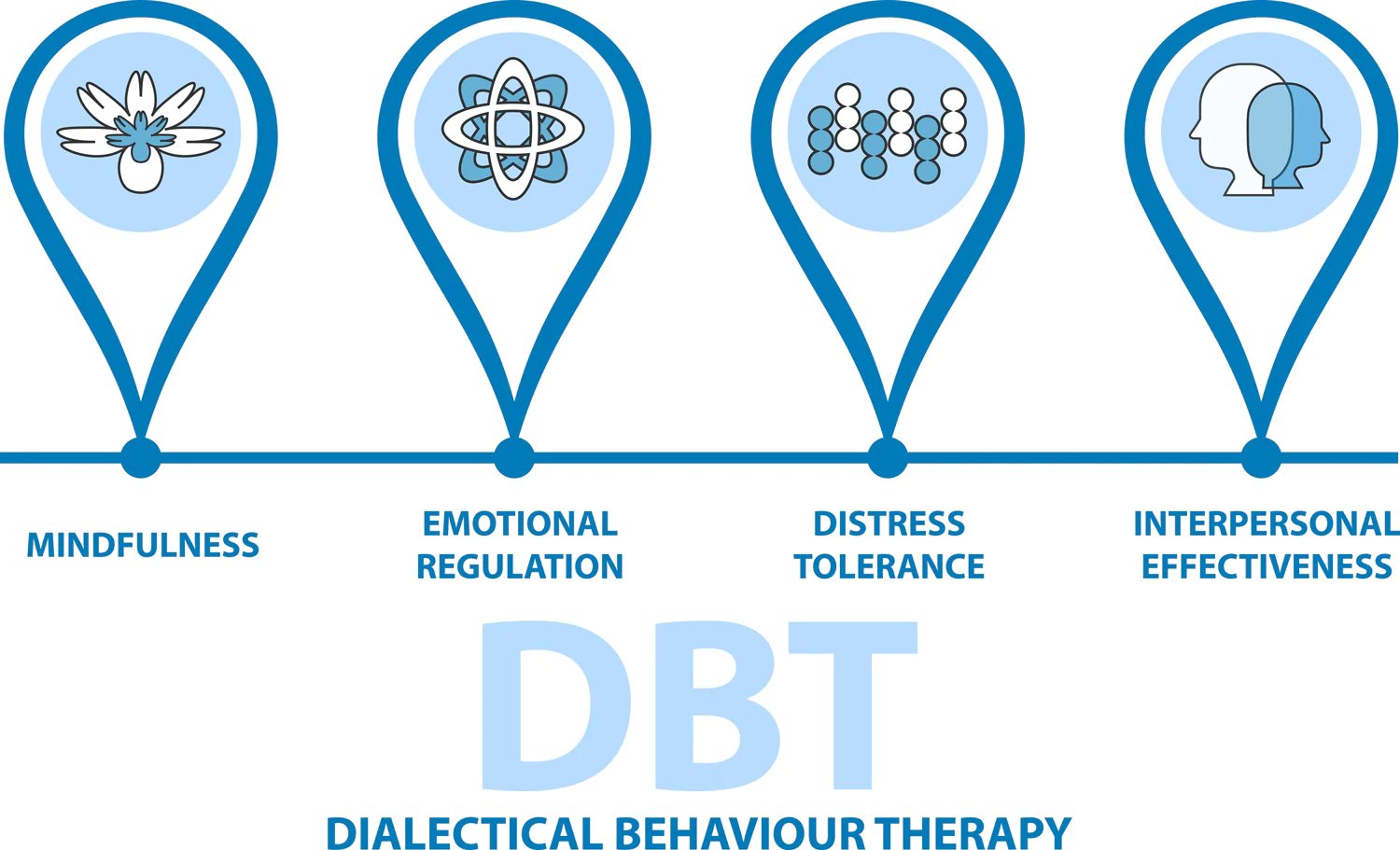
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of therapy that aims to help individuals improve their skills in four main areas: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. These skills are particularly important for people who have experienced trauma or have difficulty managing intense emotions, as they provide practical tools for coping with difficult feelings and improving relationships with others.
Trauma Therapy and PTSD
Trauma therapy is a broad term encompassing various approaches to treating psychological trauma. PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) is a common condition that arises from experiencing or witnessing traumatic events. DBT, while not exclusively a trauma-focused therapy, offers tools that can be beneficial in the context of trauma recovery. Its emphasis on emotional regulation and distress tolerance can be particularly helpful for individuals with PTSD, aiding them in managing flashbacks, anxiety, and other symptoms.
EMDR and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is another therapy used for trauma and PTSD. It involves the patient recalling traumatic events while the therapist directs their eye movements, with the aim of reducing the distress associated with traumatic memories. While EMDR focuses on reprocessing trauma, DBT emphasizes coping and living skills, making them complementary approaches.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and DBT believe in the interconnectedness of thoughts, feelings, and behavior. However, DBT differs by incorporating mindfulness and acceptance strategies. This makes DBT particularly effective for individuals who might find the direct confrontation of traumatic memories in CBT challenging.
Healing from Trauma and Coping Strategies
Healing from trauma is a complex process that often requires a multifaceted approach. DBT provides a range of coping strategies that can be vital for individuals dealing with the aftermath of traumatic events. These strategies include mindfulness exercises, which help in grounding the individual in the present moment, and distress tolerance skills, which are essential for managing intense emotional reactions.
Somatic Experiencing and Therapy Techniques
Somatic Experiencing is a body-oriented therapy that focuses on resolving the physical tension that remains in the aftermath of trauma. While DBT is more cognitive and behavioral in its approach, integrating somatic techniques can enhance its effectiveness, especially for individuals who hold trauma in their physical bodies.
Mental Health Treatment and Trauma Recovery
DBT's holistic approach makes it a valuable component of mental health treatment, particularly in the context of trauma recovery. Its focus on skill-building empowers individuals to take active steps towards healing, complementing other therapeutic techniques that might focus more on processing or re-experiencing traumatic events.
Challenges and Tradeoffs
One of the challenges in DBT and trauma therapy is balancing the need for emotional processing with the development of coping skills. While DBT provides excellent tools for managing distress, it may need to be supplemented with therapies that focus more directly on processing trauma, such as EMDR or trauma-focused CBT.
Another consideration is the individual’s readiness and capacity to engage in different types of therapy. Some may find the direct approach of EMDR or CBT overwhelming, making DBT a more suitable initial therapy. Conversely, others might require the more direct trauma processing that EMDR or CBT offers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DBT therapy is a versatile and effective approach in the realm of mental health and trauma recovery. Its emphasis on skill-building, mindfulness, and emotional regulation makes it a valuable tool in the therapeutic arsenal. However, understanding the unique needs of each individual is crucial, as is integrating DBT with other therapeutic approaches for a comprehensive treatment plan. As we continue to explore and understand the complexities of mental health and trauma, therapies like DBT play a pivotal role in providing hope and healing to those in need.